More and more companies are turning to multi-cloud environments to make their IT infrastructure more flexible, cost-efficient, and resilient. Cloud services offer advantages such as scalability, lower operating costs, and high availability. However, using various cloud services across multiple providers also increases complexity—especially when it comes to data security.
A key aspect of ensuring data security is a well-thought-out data strategy and data categorization. Companies must ensure that sensitive data is adequately protected and that compliance requirements are met. A clear strategy should be established from the outset. This blog article explores that approach.
Developing a Data Strategy
A clear and comprehensive data strategy is essential to define and regulate how data is handled within the organization. The primary goal is to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data (see Figure 1). Key elements of this strategy include:
- Data classification
- Data integrity
- Data protection
- Data access
The following sections outline the challenges of implementation and provide example measures companies can take to establish a unified data strategy.
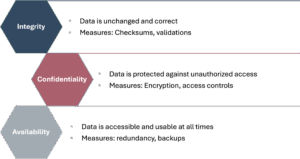
Figure 1: Data Categorization
The Importance of Data Categorization
Whether it’s GDPR, BSI Basic Protection, or ISO 27001—companies must know what data is stored and processed, and in what form. Especially during cloud migrations, precise data classification is necessary to ensure that sensitive information is not transferred or stored in a public cloud without adequate protection or encryption.
If data resides in an insufficiently protected cloud environment and a data breach occurs, companies face not only hefty fines but also a loss of trust. Violations of data protection laws, financial losses, or data leaks can also result. The damage is particularly severe if critical business secrets or confidential data fall into the wrong hands.
Challenges of Data Categorization
Data categorization presents several challenges, especially in multi-cloud environments where data is managed across various platforms:
- Data complexity: Companies generate and store vast amounts of structured and unstructured data daily—from databases to cloud documents. Uniform classification requires a well-designed concept.
- Variety of data sources and formats: Data comes from different applications, cloud services, and internal systems. The diversity of formats and storage locations complicates standardized classification and demands a cross-platform strategy.
- Consistency across cloud providers: Different cloud providers use varying security mechanisms and standards. Companies must ensure that the same security policies apply across all cloud environments, regardless of provider.
These challenges highlight the need for targeted measures to ensure a consistent approach across all cloud platforms used.
1. Clear Data Classification
A key element of implementing a data strategy is consistent data classification. Companies should review existing information policies and determine how data should be classified and what level of protection is required. If no such policies exist, they must be established. A sample classification might look like this:
| Data Class | Example | Protection Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Public Data | Company website, blog posts | No special protection required |
| Internal Data | Internal policies, org charts | Access control, backups |
| Confidential Data | Customer data, financial figures | Encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA) |
| Highly Confidential | Financial records, IP | Maximum security, Zero Trust, SIEM |
2. Define Appropriate Protection Measures
Companies must define suitable protection measures for their data and apply them consistently across all cloud platforms. The same standardized and cross-provider security policies should be established for all cloud services. Depending on the protection level, example measures include:
Technical Measures:
- Encryption of sensitive data
- Role-based access restrictions
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Use of data classification and monitoring tools
- Integration of SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solutions
Organizational Measures:
- Documentation of all security-relevant processes and regular policy updates
- Regular audits or reviews of data usage
- Ongoing employee training and awareness programs
3. Employee Training and Awareness
Training employees is a crucial step in establishing new policies within the organization. Employees play a central role in maintaining data security. Companies should conduct regular training to ensure that everyone understands how to handle (sensitive) data correctly. This includes clear guidelines and raising awareness of risks and consequences. It also reduces the risk of accidental data protection violations. When companies change their strategic cloud approach, employees must “relearn” how to manage data.
4. Technological Tool Support
Modern technologies can help companies make data categorization and classification more efficient. AI-powered solutions automatically analyze and categorize data, reducing manual effort. Examples include Microsoft Purview and AWS Macie, which use machine learning to identify sensitive data in large datasets and apply protection mechanisms.
5. Regular Review and Adjustment
Data categorization is an ongoing process. Companies should regularly review whether their classification and protection measures still meet current security requirements and adjust them as needed. Automated monitoring tools can help detect changes and trigger updates.
Conclusion – Data Categorization in Multi-Cloud Environments
A unified data strategy and standardized approach are essential for companies using multi-cloud environments. Targeted measures not only ensure compliance but also protect critical business data from unauthorized access. With a thoughtful strategy, modern technologies, and employee training, companies can effectively safeguard their data assets and minimize the risk of security breaches. Those who proactively develop a clear data strategy can unlock the full potential of modern cloud infrastructures—without compromising data security.